Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai, China
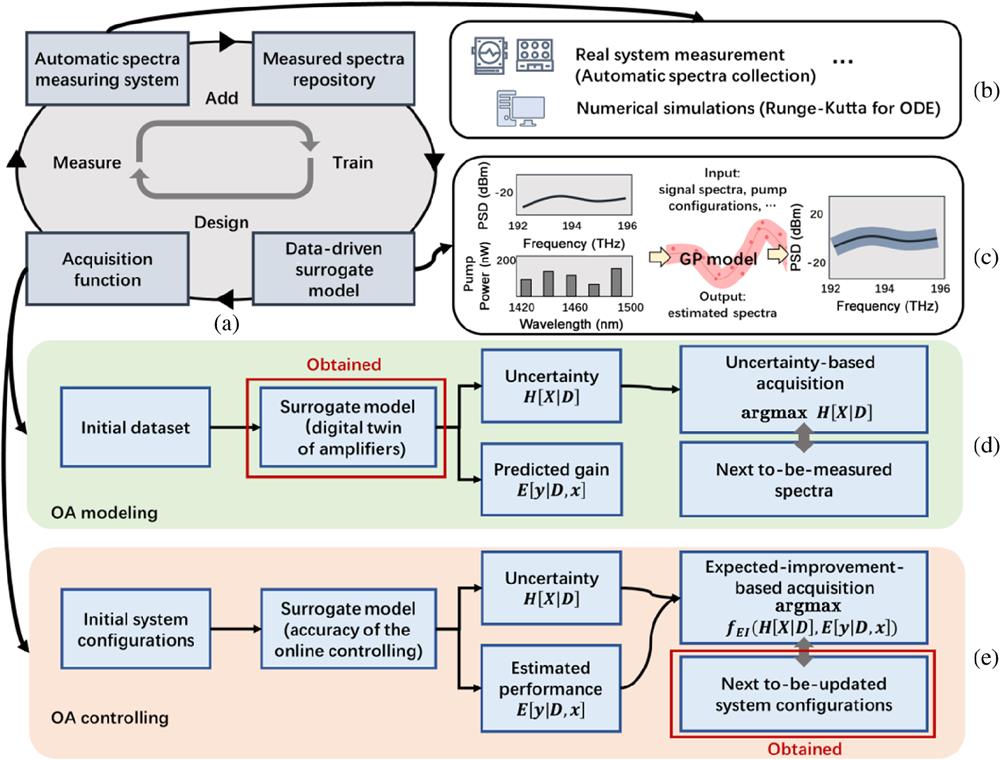
Optical networks are evolving toward ultrawide bandwidth and autonomous operation. In this scenario, it is crucial to accurately model and control optical power evolutions (OPEs) through optical amplifiers (OAs), as they directly affect the signal-to-noise ratio and fiber nonlinearities. However, a fundamental contradiction arises between the complex physical phenomena in optical transmission and the required precision in network control. Traditional theoretical methods underperform due to ideal assumptions, while data-driven approaches entail exorbitant costs associated with acquiring massive amounts of data to achieve the desired level of accuracy. In this work, we propose a Bayesian inference framework (BIF) to construct the digital twin of OAs and control OPE in a data-efficient manner. Only the informative data are collected to balance the exploration and exploitation of the data space, thus enabling efficient autonomous-driving optical networks (ADONs). Simulations and experiments demonstrate that the BIF can reduce the data size for modeling erbium-doped fiber amplifiers by 80% and Raman amplifiers by 60%. Within 30 iterations, the optimal controlling performance can be achieved to realize target signal/gain profiles in links with different types of OAs. The results show that the BIF paves the way to accurately model and control OPE for future ADONs.
optical fiber communications digital twin Bayesian inference optical amplifiers autonomous-driving optical networks Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(2): 026006
1 中国石化中原油田分公司, 河南濮阳 457001
2 长江大学地球物理与石油资源学院, 湖北武汉 430100
3 浙江大学控制科学与工程学院, 浙江杭州 310027
针对脉冲涡流技术在油气井套管检测过程中易受到环境影响而产生的噪声干扰问题, 提出一种油气井套管电磁检测数据的分段动态自适应降噪方法。通过对比分析仿真信号、实验井检测信号与实测井检测信号的差异, 结合实际检测过程中的噪声来源分析, 建立了基于偏心-抖动-温度影响因素的检测信号补偿模型。基于该补偿模型训练得到油气井套管电磁检测数据的分段动态自适应降噪模型。测井数据消噪实验结果表明, 所研究方法与常用的降噪方法相比能更好地抑制实际检测过程中偏心、抖动及温度因素带来的噪声影响, 具有应用和借鉴价值。
无损检测 油田套管 电涡流 降噪 non-destructive testing oil field casing eddy current noise reduction 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报
2023, 21(9): 1156
吉林大学电子科学与工程学院集成光电子学国家重点实验室,吉林 长春 130012
光热治疗以其无创性、非侵入性、副作用小等特点受到了广泛关注。二维碳化钛(MXene)作为一种新型纳米材料,具有优异的物理和化学性能,其中包括良好的光热效应。本课题组通过静电吸附作用构建了基于MXene的光热/化疗协同治疗纳米试剂,该纳米试剂具有优异的消光系数[24.05 L/(g·cm)]以及出色的光热转效率(31.34%)。体外细胞实验结果表明该纳米对HepG2细胞起到了良好的抑制效果,经其治疗后的细胞存活率仅为21.09%。
医用光学 光热治疗 MXene 化疗 近红外光 纳米材料
针对在深度估计过程中的遮挡问题,提出一种新的基于多线索融合的光场图像深度估计方法。利用约束性自适应散焦算法和约束性角熵度量算法获取场景的散焦线索、一致性线索,并计算出场景的初始深度、置信度。为增强图像的边缘轮廓信息,通过Canny算子提取中心视角图像的边缘信息,然后利用马尔可夫随机场融合场景的初始深度、置信度及边缘信息,实现图像的高精度深度估计。与其他先进方法相比,所提方法能够较好地解决场景中存在的遮挡问题,获取的深度图精度较高、平滑效果较好,图像边缘保持效果较好。
图像处理 四维光场 深度估计 遮挡 多信息融合
郑州大学 物理工程学院, 河南 郑州 450001
菲涅耳非相干相关全息术(Fresnel Incoherent Correlation Holography, FINCH)属于同轴全息系统, 需要通过相移技术去除零级像和共轭像。通过对FINCH系统记录及再现过程的理论分析, 根据系统点扩散函数推导出了n步相移数学计算公式, 模拟仿真了相移步数n对FINCH系统成像质量的影响, 并搭建了非相干光反射式数字全息记录系统, 对模拟结果进行了实验验证。模拟仿真及实验结果表明: 通过增加相移步数不能显著提高再现像质量; 二步相移能够提高记录速度, 通过去除原始图像和小波分解的方法可以抑制零级像, 提高再现像质量; 通过对三步相移每个相移全息图拍摄多次求平均值后得到的再现像与拍摄一次得到的再现像对比发现, 随着拍摄次数的增加, 得到的再现像质量越来越好, 背景噪声大大减弱, 再现像强度越来越大, 为FINCH系统再现像质量的改善提供了新的思路和新的实验基础。
全息术 菲涅耳非相干相关全息术 相移技术 小波分解 holography Fresnel incoherent correlation holography phase-shifting technology wavelet decomposition 红外与激光工程
2019, 48(8): 0825001
郑州大学 物理工程学院, 河南 郑州 450001
针对光场深度估计过程中数据量大、边缘处深度估计结果不准确问题, 利用压缩感知原理重建光场, 提出一种新的多信息融合的光场图像深度估计算法。利用压缩感知重建算法重建5×5视角光场数据, 获取光场数据后首先移动子孔径实现重聚焦, 然后利用角度像素块散焦线索和匹配线索计算出场景初始深度和置信度。计算图像边缘信息, 通过融合初始深度、置信度、边缘信息获取最终深度。实现压缩光场仿真重建, 并对仿真光场数据和公开光场数据进行深度估计, 实验结果表明: 可以仿真重建出5×5视角光场数据, 且仿真重建的光场可用于深度估计。该深度估计算法在场景边缘处的深度估计结果边界清晰, 层次分明, 验证了重建光场深度估计的可行性与准确性。
应用光学 深度估计 压缩感知 光场重建 applied optics depth estimation compressed sensing light field reconstruction
长春理工大学高功率半导体激光国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130022
利用等离子体增强原子层沉积系统, 以逐层刻蚀方式对GaSb进行氮(N)钝化处理, 研究了钝化过程中刻蚀周期对GaSb钝化效果的影响。研究结果表明, 当刻蚀周期数为200时, 钝化效果最好; 刻蚀周期数不足(100)时, 钝化效果最弱; 刻蚀周期数较高(300~400)时, 随着刻蚀周期数的增大, 钝化效果减弱。
材料 光致发光 N钝化 刻蚀周期

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 DTU Fotonik, Technical University of Denmark, 2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark
2 Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research, Ackermannweg 10, 55128 Mainz, Germany
3 Department of Physics, Bilkent University, 06800 Ankara, Turkey
4 National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Institute of Power Engineering, 30 Lenin Avenue, 634050 Tomsk, Russia
5 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Bilkent University, 06800 Ankara, Turkey
6 Biophotonics Imaging Laboratory, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, Illinois 61801, USA
7 Fakult?t für Physik, Universit?t Duisburg-Essen, Lotharstra?e 1, 47048 Duisburg, Germany
The emission wavelength of a laser is physically predetermined by the gain medium used. Consequently, arbitrary wavelength generation is a fundamental challenge in the science of light. Present solutions include optical parametric generation, requiring complex optical setups and spectrally sliced supercontinuum, taking advantage of a simpler fiber technology: a fixed-wavelength pump laser pulse is converted into a spectrally very broadband output, from which the required resulting wavelength is then optically filtered. Unfortunately, this process is associated with an inherently poor noise figure, which often precludes many realistic applications of such supercontinuum sources. Here, we show that by adding only one passive optical element—a tapered photonic crystal fiber—to a fixed-wavelength femtosecond laser, one can in a very simple manner resonantly convert the laser emission wavelength into an ultra-wide and continuous range of desired wavelengths, with very low inherent noise, and without mechanical realignment of the laser. This is achieved by exploiting the double interplay of nonlinearity and chirp in the laser source and chirp and phase matching in the tapered fiber. As a first demonstration of this simple and inexpensive technology, we present a femtosecond fiber laser continuously tunable across the entire red–green–blue spectral range.
(140.3538) Lasers pulsed (140.3510) Lasers fiber (140.3600) Lasers tunable (190.4370) Nonlinear optics fibers (060.7140) Ultrafast processes in fibers (140.7300) Visible lasers. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000750
在对散射介质散射特性进行分析的基础上,提出了一种对散射介质中物体进行单像素成像的方法,基于数字微镜阵列和单点探测器,设计并搭建了相应的单像素成像系统。通过对数字微镜阵列加载一系列具有不同相位的条纹图案,采集对应的光强信息,结合图像恢复算法,实现了对位于散射介质中的物体成像。为了去除噪声,分析了噪声的来源,设计了滤波器对所拍摄的物体图像进行滤波处理,图像质量得到了显著提高。与传统散射介质成像系统相比,该系统结构简单,无需复杂的标定过程,在多个领域具有应用前景。
成像系统 单像素成像 散射介质 四步相移 数字微镜阵列
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Terahertz wave detecting method based on multi-reflection optical lever with nano-scale displacement measuring precision is presented. Multi-reflection optical lever is composed of a pair of plane micro-mirrors, and detecting material is coated on one mirror to absorb terahertz radiation. Affected by radiant thermal effects, tiny mirror deformation is produced while displacement between mirrors is changed. These variations proportional to radiation are amplified and measured by multi-reflection optical lever, and then terahertz wave power can be obtained. Theoretical displacement measuring precision of multi-reflection optical lever method is better than 1 nm. Experimental results show that measuring stability of this method is better than Knife-edge filter method. This method achieves resolution of 4 nm, sensitivity of 5.95 nm/mV, and measurement range of 30 \mu m.
040.0040 Detectors 120.1880 Detection 040.2235 Far infrared or terahertz 040.6808 Thermal (uncooled) IR detectors, arrays and imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s2): S20402





